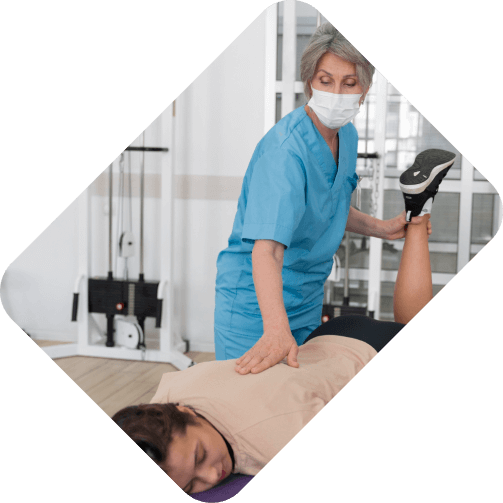
Functional Neurosurgery Procedures
- Op. Dr. Mehmet Beşir Sürme
- Functional Neurosurgery Procedures

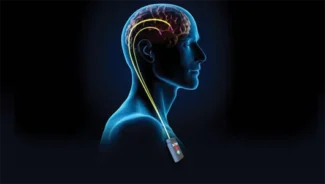
Deep Brain Stimulation
Deep Brain Stimulation / Electrode Surgery
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a treatment for movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, dystonia, and essential tremor, involving the delivery of electrical signals to specific areas of the brain via implanted electrodes to improve motor function. DBS enhances quality of life in patients who do not respond to medication.
Epilepsy Surgery
Sara Surgeries / Seizure Source Surgery
In patients with drug-resistant epilepsy, it involves preventing seizures by identifying and removing seizure foci or severing their connections. The focus is identified through preoperative EEG, MRI, and neuropsychological tests.
Vagus Nerve Stimulation
Vagus Nerve Stimulation / Pain and Epilepsy Stimulator
It involves reducing the frequency of epileptic seizures or controlling certain chronic pains by delivering electrical stimulation to the vagus nerve in the neck region using an electrode. A small battery system is usually surgically implanted.
Peripheral Neuromodulation
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation / Pain Stimulator
In conditions such as nerve-related chronic pain or migraine, it involves regulating pain transmission by placing electrodes on peripheral nerves and delivering electrical stimulation. Temporary or permanent applications are possible.
Stereotactic Surgery
Brain Surgery with Precision Targeting
It is a surgical method that enables the accurate and minimally invasive treatment of small targets within the brain using three-dimensional coordinates. It is commonly used in tumor biopsy, radiosurgery, or deep brain stimulation planning.
Function-Preserving Surgery for Brain Tumors
Functional Mapping for Tumor Resection
It involves safely removing the tumor while preserving brain function through awake surgery or intraoperative neuromonitoring, particularly in tumors near language, motor, or sensory areas.
Baclofen Pump
Intraspinal Muscle Relaxant Pump Application
Baclofen is a medication that reduces muscle spasms and stiffness. It is used especially in the treatment of spasticity (e.g., following stroke, multiple sclerosis, cerebral palsy).
The intrathecal baclofen pump delivers the medication directly into the spinal cord, making it both more effective and minimizing systemic side effects. The pump is implanted under the skin and can be surgically programmed; the dose is customized for each patient.
Bladder Stimulator
Bladder Nerve Stimulation / Battery Regulating Urinary Function
In patients with urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, or bladder emptying problems, bladder functions are regulated by delivering electrical stimulation via electrodes placed on the sacral nerves.
A two-step procedure is usually performed: the effect of the stimulation is evaluated using a temporary test electrode, and if successful, a permanent implant is placed. This provides a significant improvement in patients' quality of life.
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
Treatment with External Magnetic Stimulation
TMS is a non-invasive method that alters brain activity by delivering electrical stimuli to the brain cortex through magnetic fields applied over the skull.
Main areas of use:
– Treatment for depression and anxiety
– Alleviating motor symptoms in Parkinson's disease
– Pain syndromes and migraines
TMS treatment is usually administered in weekly sessions and does not require surgical intervention.
Stem Cell Therapy
Nerve Repair and Regeneration
Stem cells are cells that can contribute to the regeneration of damaged brain or spinal cord tissue and functional recovery.
Application areas:
– Spinal cord injuries
– Neurodegenerative diseases
– Neurological recovery after stroke
Stem cells are mostly administered intravenously, intrathecally, or directly into the lesion site via injection. Research is ongoing, and safe and effective protocols are being developed.
Ozone therapy
Ozone Applications via Blood, Tissue, and Injection
Ozone gas regulates cellular metabolism, increases blood circulation, and reduces inflammation when used in controlled doses for medical purposes.
Main application areas:
– Lumbar and cervical disc herniation, joint pain
– Chronic pain and degenerative joint diseases
– Anti-aging and immune-boosting treatments
Application methods include intravenous ozone, rectal insufflation, local injection, and topical application.
- International Experience
- Modern and Innovative Treatments
- Scientific Competence
- Trust and Patient-Centered Approach

Frequently Asked Questions About Functional Neurosurgery
How Does Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) Offer a Solution for Movement Disorders (Parkinson's, Tremor) That Do Not Respond to Drug Treatment?
Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) for Movement Disorders Unresponsive to Medication (Parkinson's, Tremor) NasDeep Brain Stimulation (DBS) is a treatment designed for patients with movement disorders such as Parkinson's disease, dystonia, and essential tremor whose symptoms cannot be controlled with medication. During this surgical procedure, electrodes are precisely placed in specific targets of the brain responsible for movement (using stereotactic surgery). Continuous electrical stimulation through these electrodes improves motor functions. DBS significantly alleviates symptoms such as tremor, rigidity, and slowness, thereby improving the patient's quality of life. Does It Offer a Solution?
What Are the Implantable Systems Used in the Treatment of Drug-Resistant Epilepsy and Chronic Pain?
Neurostimulation (Pacemaker Systems) plays a critical role in the treatment of uncontrollable epilepsy and chronic pain. There are two main types of pacemaker applications: Vagus Nerve Stimulation (VNS): A pacemaker system is placed on the vagus nerve in the neck region, and regular stimulation is applied to reduce the frequency and severity of epileptic seizures. Peripheral Neuromodulation (Pain Stimulator): In cases of chronic pain (e.g., migraine or nerve pain), an electrode is placed on the relevant nerve to regulate the transmission of pain signals. These pacemaker systems are surgically programmable and are placed in a way that is not visible from the outside, regulating neurological functions.
How is Severe Muscle Stiffness (Spasticity) Following Stroke, Multiple Sclerosis (MS), or Cerebral Palsy Treated?
Severe spasticity (uncontrollable muscle stiffness) that develops after conditions such as stroke, MS, spinal cord injuries, or cerebral palsy is effectively treated with a Baclofen Pump. In this method, a small pump containing the muscle relaxant drug Baclofen is placed under the skin, and the drug is delivered directly into the spinal fluid (intrathecally) via a catheter. This application enhances the drug's effect on muscle spasms while minimizing its systemic side effects and significantly improving patients' mobility and comfort.

CORRECT DIAGNOSIS CORRECT TREATMENT
We proudly offer scientific and high-quality treatments.
Approach in accordance with International Standards
International Standards Approach: With its experience in pediatric brain surgery in Rome and numerous scientific publications, it applies evidence-based medicine in every treatment.
Patient-Centered Care
They personalize treatment plans according to their patients' needs, providing reassuring and transparent communication throughout the process.